
Reflectors use a large concave spherical mirror (primary mirror or objective mirror) to gather light and bring it to focus on a small, optically flat mirror near the front of the telescope tube. This type of telescope is called a "reflector" or catropic telescope. By 1681, the noted early physicist Sir Issac Newton invented a telescope using a large mirror as a light-collecting surface rather than a lens. The limitations and chromatic aberrations of the refractor began to lead early astronomers to look for other solutions to the problems of building large-aperture telescopes. Refractors can be very frustrating telescopes for taking pictures. The longer the focal ratio of the telescope becomes, the longer exposure times are required for imaging a given object. Long focal lengths are also tough for astrophotography work. The long focal lengths produce very narrow fields of view that cannot contain entire deep sky objects. Refractors do have other limitations as well. Fluorite lenses however are not subject to the chromatic aberrations that plague glass lens refractors. Calcium fluorite is not glass, but a mineral that must be ground and polished in a very time-consuming and expensive procedure. For those who desire perfect color in their images, the closest you can get is a telescope with a calcium fluorite lens element. To try to minimize the effects of this color distortion, the telescopes lenses may be coated with metallic-based compounds that also improve overall light transmission. Objects viewed through a refractor will often have a fringe of false color surrounding them caused by the optical separation of the differing wavelengths of light through the telescope objective lens. This causes an error known as chromatic aberration. As light passes through the glass lenses, the colors are separated in the same way that a prism might and not transmitted evenly by the lens elements.
Refractors also are subject to an error that is an inherent byproduct of the design. In some loss of image sharpness and they don't get any lighter. F-ratio is the focal length divided by the diameter of the objective. Lenses can be designed that provide a shorter focal length,but that resultsħ Focal length is the distance from the objective lens to the point at which light rays come to focus. By the time the scope reaches about 4 inches (100 mm) in diameter, the objective lens starts to become too heavy and the tube too long for use in a design that can still be considered portable.

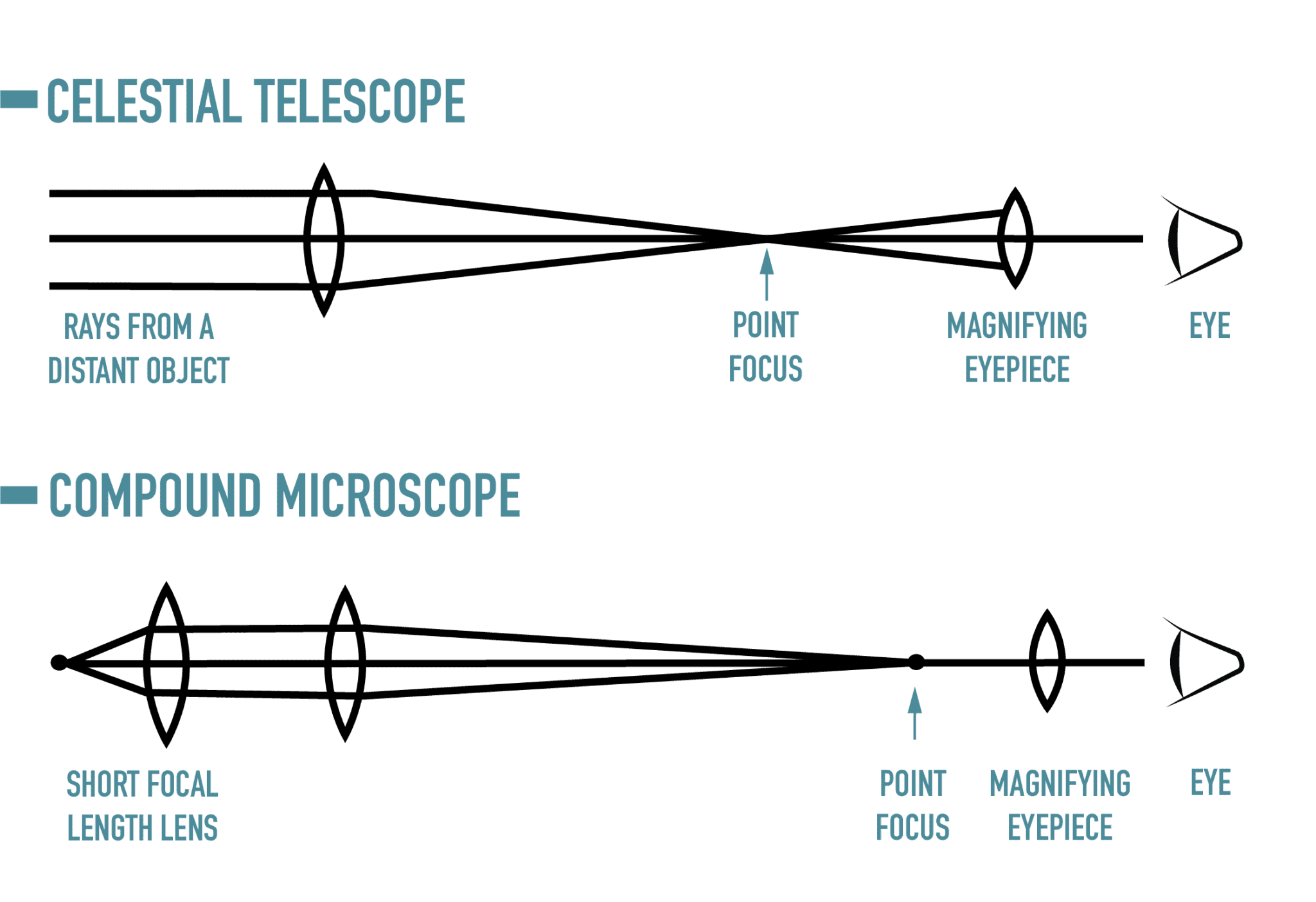
The refractor does have some drawbacks that prevent it from being used as a design for large-aperture telescopes. These long-focus telescopes provide sharp images with high magnification without using excessively short focal-length eyepieces.

The refractor lenses generally are of long focal length, often producing f ratios7 of f/12 to f/14. The lenses never need to be adjusted and are in fact often cemented in place. For an amateur shopping for a telescope, the chief advantage of a refractor is that its lenses are rigidly held in place in the telescope tube making the telescope virtually maintenance free. Science has refined the design of the refractor over the years allowing it to create sharper images with better focus. It would be nearly 400 years before the church would come to admit it early in the reign of Pope John Paul II when Galileo was formally brought back into the Roman Catholic Church.

The Sun was at the center of the solar system and all the planets circled it. The church would torment him, ruin him, excommunicate him and finally forced him to recant. Earth was not at the center of the solar system, but the Sun was! Galileo would pay dearly for his blasphemy. These discoveries led Galileo to realize that the geocentric model of the solar system was incorrect. With this simple design, Galileo discovered that Venus exhibited phases like the Moon and that Jupiter had satellites circling it. In any telescope the objective is the lens or mirror element that gathers starlight and directs it to a focus point. The lens at the front of the scope is called the objective. That original telescope used a simple convex lens to gather and focus light and a concave lens at the opposite end of the tube to bring that light to a crude focus. This design, also called a dioptric telescope, is based directly upon the original opera glass telescope designed by Galileo in 1610. The telescope you own now is most likely a refractor. Now that you have made the decision to step up to a medium to large aperture telescope from your department store model, you need to consider the various types of optical designs and decide what best suits your needs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
